Cybersecurity threats are escalating, with the average cost of a data breach reaching $4.45 million in 2023, according to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report. As organizations strive to protect their data and maintain customer trust, two prominent security frameworks have emerged: NIST CSF and ISO 27001.
Both frameworks aim to help organizations establish a robust cybersecurity posture, but they differ in their approaches and implementation. As you navigate the complex landscape of cybersecurity, understanding the differences between these frameworks is crucial for making informed decisions about your organization’s security strategy.
By exploring the origins, purposes, and core components of NIST CSF and ISO 27001, you’ll be better equipped to determine which framework aligns best with your organization’s needs and how they can work together to enhance your security posture.
Key Takeaways
- Understand the primary objectives and benefits of NIST CSF and ISO 27001.
- Learn about the key differences between the two frameworks.
- Discover how to choose the most suitable framework for your organization.
- Explore the potential for integrating both frameworks to strengthen your security.
- Gain insights into the implementation and certification processes for each framework.
Understanding Security Frameworks
To effectively manage cybersecurity risks, organizations need to comprehend the role of security frameworks in their overall security strategy. Prior to establishing a standard, it is imperative for firms to comprehend the reasons behind any shortcomings in their information security systems.
If implemented without considering organizational needs, security frameworks like NIST CSF or ISO 27001 can potentially make companies less secure. Therefore, understanding the importance of these frameworks is crucial.
The Importance of Security Frameworks in Today’s Business Environment
Security frameworks are essential in today’s business environment due to the increasing sophistication and evolution of cyber threats. Ad-hoc security measures often fail to provide adequate protection against these threats. A structured approach to security helps organizations maintain consistency across different departments and locations, ensuring that no vulnerabilities are overlooked.
- Adopting a structured security approach enables organizations to maintain consistency across various departments and locations.
- Security frameworks help organizations meet regulatory requirements and industry standards while demonstrating due diligence to stakeholders.
- A structured approach allows for better resource allocation by identifying the most effective security controls for specific organizational risks.
Why Organizations Need Structured Approaches to Security
Organizations need structured approaches to security to effectively manage cybersecurity risks and protect their information security. A structured approach provides a foundation for continuous improvement in security practices, allowing organizations to mature their security programs over time.
- Structured approaches help organizations identify and address vulnerabilities more effectively.
- By implementing a security framework, organizations can ensure a comprehensive risk management approach.
- This, in turn, enables organizations to demonstrate their commitment to security to customers, partners, and stakeholders.
What is NIST CSF?
NIST CSF provides a comprehensive approach to cybersecurity, helping organizations identify, protect, detect, respond to, and recover from cyber threats. This framework is designed to be flexible and adaptable, making it suitable for organizations of all sizes and types.
Origin and Purpose of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework
The NIST CSF was developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in response to Executive Order 13636, “Improving Critical Infrastructure Cybersecurity,” issued in 2013. The primary purpose of the NIST CSF is to provide a common language and framework for organizations to manage and reduce cybersecurity risk.
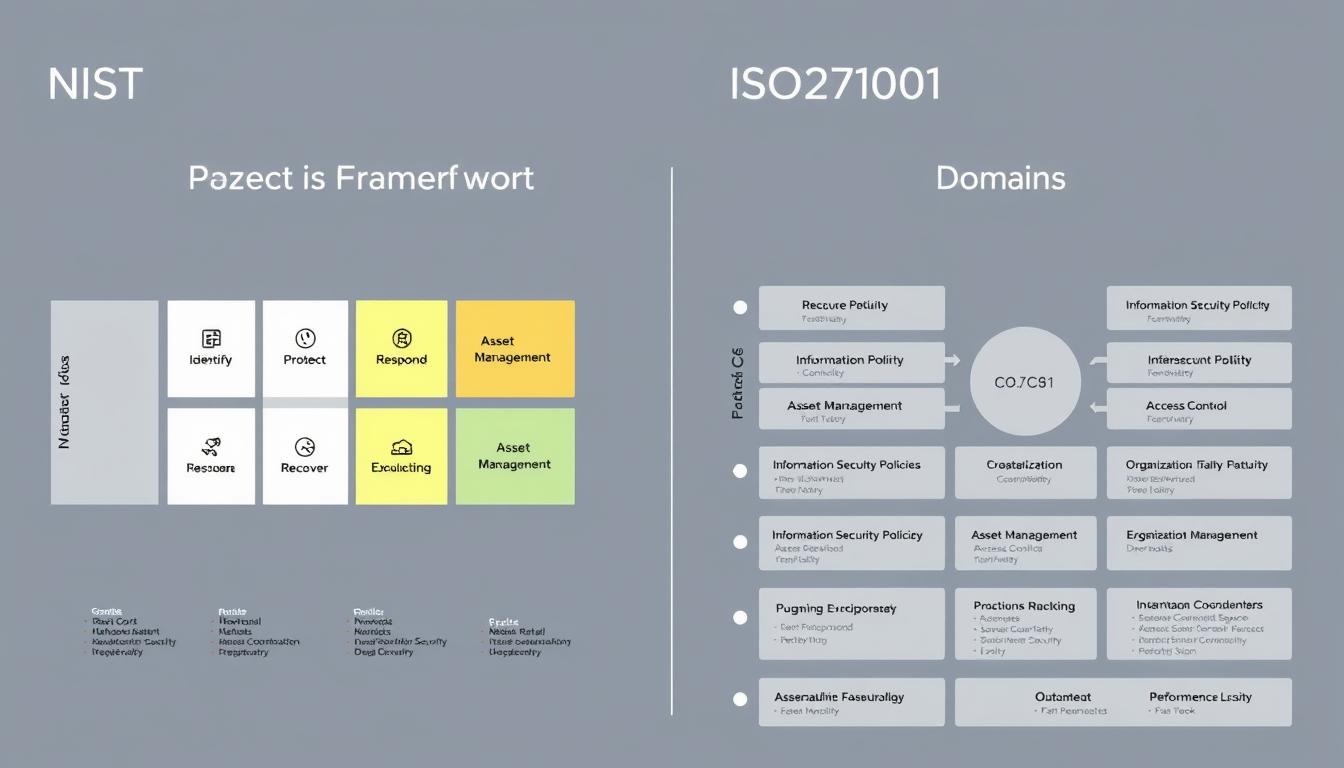
The 5 Core Functions of NIST CSF
The NIST CSF is structured around five core functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. These functions provide a comprehensive approach to managing cybersecurity risk.
Identify Function
The Identify function involves identifying the organization’s critical infrastructure and assets, as well as understanding the potential risks and threats to those assets. This includes developing a thorough understanding of the organization’s cybersecurity risks and developing strategies to manage those risks.
Protect Function
The Protect function focuses on implementing measures to prevent or deter cyber attacks. This includes implementing robust security controls, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption.
Detect Function
The Detect function involves implementing measures to detect cyber attacks in real-time. This includes monitoring network traffic, system logs, and other security-related data to identify potential security incidents.
Respond Function
The Respond function involves taking action during or immediately after a cybersecurity incident. This includes developing incident response plans, conducting regular training exercises, and implementing measures to contain and mitigate the incident.
Recover Function
The Recover function is critical to maintaining business continuity after a cybersecurity incident. It involves establishing a plan to restore capabilities and maintain resilience. This includes strategies like recovering potentially deleted or corrupted data using a backup, repairing damaged equipment, revising policies to prevent future breaches, and updating customers and other affected parties about the progress.
The Recover function helps your organization develop and implement appropriate activities to maintain plans for resilience and to restore any capabilities or services that were impaired due to a cybersecurity incident. Effective recovery planning helps minimize downtime and business impact following security incidents.
- The Recover function includes three categories: Recovery Planning, Improvements, and Communications.
- Testing recovery procedures before they’re needed helps ensure they’ll work effectively during actual incidents.
- The recovery process provides valuable opportunities to strengthen your security posture and prevent similar incidents in the future.
Benefits of Implementing NIST CSF
Enhancing cybersecurity with NIST CSF is a prudent decision for forward-thinking organizations. By adopting this framework, you can significantly improve your security posture and better manage cybersecurity risks. The benefits of NIST CSF implementation are multifaceted, ranging from enhanced flexibility to cost-effectiveness.
Flexibility and Adaptability
One of the key advantages of NIST CSF is its flexibility and adaptability. This framework allows organizations to tailor their cybersecurity practices to their specific needs and risk profiles. You can implement NIST CSF at your own pace, integrating it with existing security measures to create a robust cybersecurity program.
Cost-Effectiveness and Accessibility
NIST CSF is available free of charge, making it an accessible option for organizations of all sizes. Its voluntary nature means you can implement it according to your budget and resources. By prioritizing security investments based on risk, you can ensure the most effective use of your security budget.
Implementing NIST CSF can also help reduce costs associated with security incidents by enhancing prevention, detection, and response capabilities. The framework’s common language and structure facilitate streamlined communication about security within your organization and with external partners, reducing overhead costs.
Moreover, NIST CSF helps you avoid duplicative or ineffective security controls, thereby optimizing your security resources and investments.
What is ISO 27001?
In the realm of information security, ISO 27001 stands out as a premier standard that helps organizations protect their data assets. This international standard provides a framework for implementing an Information Security Management System (ISMS) that is tailored to an organization’s specific needs.
Background and Purpose of ISO 27001
ISO 27001 was developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) to provide a globally recognized framework for managing information security. The standard is designed to help organizations of all sizes and types protect their information assets from various threats and vulnerabilities.
The primary purpose of ISO 27001 is to provide a systematic approach to managing sensitive information and ensuring its confidentiality, integrity, and availability. By adopting this standard, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to information security and maintain the trust of their stakeholders.
The 3 Core Principles of ISO 27001
ISO 27001 is built around three core principles that form the foundation of an effective ISMS: confidentiality, information integrity, and availability of data. These principles are crucial for ensuring that an organization’s information assets are properly protected.
Confidentiality
The principle of confidentiality ensures that sensitive information is only accessible to authorized individuals or systems. This involves implementing controls such as access management, encryption, and non-disclosure agreements to prevent unauthorized access or disclosure.
Information Integrity
Information integrity is about ensuring that data is accurate, complete, and not modified without authorization. Controls such as data validation, backup procedures, and version control help maintain the integrity of an organization’s information assets.
Availability of Data
The final principle of ISO 27001 is the availability of the organization’s data. This principle dictates that employees and clients must be able to access the data they need for business purposes, but only if they are authorized to do so. Ensuring data availability involves several key measures:
- Implementing redundancy and backup systems to prevent data loss
- Developing disaster recovery planning and business continuity management strategies
- Balancing security controls with the need for efficient access to information resources
- Maintaining operations during disruptions, whether caused by technical failures, natural disasters, or security incidents
By focusing on these three core principles, ISO 27001 helps organizations implement a robust ISMS that protects their information assets and supports their business objectives.
Benefits of ISO 27001 Certification
The benefits of ISO 27001 certification extend beyond compliance to enhance your organization’s overall security and credibility. By adopting this international standard, you not only bolster your information security management system (ISMS) but also gain a competitive edge in the market.
International Recognition and Credibility
ISO 27001 is recognized globally as a benchmark for information security management. Achieving certification demonstrates your organization’s commitment to protecting sensitive information, thereby enhancing your reputation among customers, partners, and stakeholders. This international recognition can be a significant differentiator in a competitive business landscape.
Comprehensive Risk Management Approach
ISO 27001 provides a structured methodology for identifying, assessing, and treating information security risks. This risk-based approach enables your organization to focus security resources on the areas that matter most to your business. By implementing ISO 27001, you’ll be able to identify threats and vulnerabilities that might otherwise be overlooked, ensuring a more robust security posture.
The standard’s comprehensive risk management process involves three key steps: identifying risks to your organization’s information, implementing controls appropriate to the risk, and monitoring their performance. This proactive approach to risk management helps ensure that your security measures are always aligned with the evolving threat landscape.
- A structured methodology for identifying and assessing information security risks
- A risk-based approach that helps focus security resources on critical areas
- Continuous improvement cycle that ensures your risk management approach evolves with changing threats and business requirements
- Integration with your organization’s broader enterprise risk management activities, creating a more holistic view of organizational risk
By adopting ISO 27001, you can ensure that your organization’s information security practices are aligned with international best practices, enhancing both security and credibility.
NIST CSF vs. ISO 27001: What’s the difference?
NIST CSF and ISO 27001 are two prominent cybersecurity frameworks that serve different purposes, despite some similarities. Understanding their differences is crucial for organizations to choose the most suitable framework for their cybersecurity needs.
Scope and Focus
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) is primarily focused on managing and reducing cybersecurity risk, providing a comprehensive framework for organizations to understand and improve their cybersecurity posture. In contrast, ISO 27001 is an international standard that specifies the requirements for an information security management system (ISMS), emphasizing the implementation of a systematic approach to managing sensitive information.
NIST CSF is often adopted by organizations in the United States, particularly those in critical infrastructure sectors, due to its flexibility and adaptability. On the other hand, ISO 27001 is widely recognized and adopted globally, offering a more prescriptive approach to information security management.
Structure and Approach
The structure and approach of NIST CSF and ISO 27001 differ significantly. NIST CSF is organized around five core functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. This framework provides a flexible, risk-based approach to cybersecurity. In contrast, ISO 27001 follows the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle and is centered around the implementation of an ISMS, with a strong emphasis on risk management and continuous improvement.
Certification Process
One of the key differences between NIST CSF and ISO 27001 lies in their certification processes. NIST CSF is voluntary and does not require certification, making it more accessible to organizations. Conversely, ISO 27001 offers a certification option, which involves a rigorous audit process by a third-party auditor, providing an additional layer of credibility and assurance.
Cost Considerations
Becoming ISO 27001 compliant is generally more expensive than adhering to the NIST CSF, primarily due to the certification requirements. The cost of ISO 27001 certification can range from $5,000 to $15,000 or more, depending on the organization’s size and complexity. While NIST CSF is free to access and implement, both frameworks incur additional costs related to implementation, such as engineering time, administrative efforts, software tools, and employee training.
- The direct costs of implementing NIST CSF are typically lower than ISO 27001 due to the absence of certification requirements.
- ISO 27001 implementation and certification involve various cost components, including consulting fees, certification audit costs, and ongoing surveillance audits.
- Organizational size, complexity, and existing security maturity significantly affect the total cost of implementing either framework.
- Evaluating the return on investment for both frameworks involves considering implementation costs and potential benefits, such as reduced security incidents and increased business opportunities.
- Organizations with limited budgets may start with NIST CSF and transition to ISO 27001 as resources become available.
Similarities Between NIST CSF and ISO 27001
A closer look at NIST CSF and ISO 27001 reveals that they have more in common than initially meets the eye, particularly in terms of risk management and security controls. Many organizations are surprised to learn that implementing one of these frameworks can significantly advance their compliance with the other.
Shared Risk Management Principles
Both NIST CSF and ISO 27001 are built around robust risk management principles. They emphasize the importance of identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks to an organization’s information assets. By adopting a risk-based approach, organizations can better protect themselves against evolving cyber threats.
Key similarities in their risk management approaches include:
- Emphasis on risk assessment and mitigation
- Importance of continuous monitoring and review
- Need for a structured and systematic approach to risk management
Overlapping Controls and Requirements
A significant overlap exists between the controls and requirements outlined in NIST CSF and ISO 27001. For instance, both frameworks stress the importance of access control, asset management, incident response, and security awareness training. By understanding these overlaps, organizations can avoid duplicating efforts and streamline their compliance processes.
Some of the common control areas include:
- Access control and identity management
- Asset management and inventory
- Incident response planning and execution
- Security awareness and training programs
By recognizing the similarities between NIST CSF and ISO 27001, organizations can develop a more integrated approach to managing their cybersecurity posture. This not only enhances their security but also reduces the complexity and cost associated with compliance.
How to Choose Between NIST CSF and ISO 27001
Choosing between NIST CSF and ISO 27001 can be a daunting task, but understanding your organization’s specific needs is key. When evaluating these frameworks, consider factors such as your organization’s maturity level, business requirements, and available resources.
Organizational Maturity Considerations
Your organization’s maturity level plays a significant role in determining which framework is more suitable. If your organization is just starting to develop its cybersecurity practices, theNIST CSFmight be a more appropriate choice due to its flexibility and adaptability. On the other hand, if your organization has already established a robust security program and is looking for a more structured approach to achieve international recognition,ISO 27001 certificationmight be the better option.
Assessing your organization’s maturity involves evaluating its current security controls, policies, and procedures. This assessment will help you identify gaps and areas for improvement, allowing you to choose a framework that aligns with your organization’s needs.
Business Requirements and Objectives
Your business requirements and objectives are crucial in deciding between NIST CSF and ISO 27001. If your organization operates in a highly regulated industry or handles sensitive customer data, achievingISO 27001 certificationmight be necessary to demonstrate your commitment to information security to stakeholders and customers. In contrast, if your organization is looking for a framework that provides a flexible and cost-effective approach to managing cybersecurity risk, theNIST CSFcould be more suitable.
Consider your organization’s short-term and long-term objectives when making this decision. For instance, if you’re planning to expand your business globally, having an ISO 27001 certification can provide a competitive edge due to its international recognition.
Resource Availability and Budget Constraints
Implementing either framework requires significant resources, including budget, personnel, and time. Becoming ISO 27001 compliant is generally more expensive than adhering to the NIST CSF, mainly due to the cost of hiring a third-party auditor for certification. The cost of ISO 27001 certification can range from $5,000 to $15,000 or more, depending on the complexity of your organization’s security program.
To realistically assess your organization’s available resources, consider the costs associated with implementing and maintaining either framework. This includes engineering time, administrative costs, software tools, and employee training. You can explore strategies like phased implementation or focusing on high-priority controls first to manage these costs effectively.
For more detailed information on the differences between NIST CSF and ISO 27001, you can visit this resource, which provides a comprehensive comparison of the two frameworks.
By carefully evaluating your organization’s maturity, business requirements, and available resources, you can make an informed decision between NIST CSF and ISO 27001. Additionally, leveraging automation tools and compliance software can help reduce the resource burden associated with implementing and maintaining either framework.
Using NIST CSF and ISO 27001 Together
By adopting both NIST CSF and ISO 27001, organizations can achieve a more balanced and effective cybersecurity program. This combined approach allows you to leverage the strengths of both frameworks, creating a more robust security posture.
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework (NIST CSF) and ISO 27001 are built on widely accepted best practices in cybersecurity, with many overlapping practices and protocols. If you’ve implemented NIST CSF, you’re already about 80% of the way to ISO 27001 compliance, and ISO 27001 contains over half of the NIST CSF guidelines.
Benefits of a Combined Approach
Implementing both frameworks can provide more comprehensive coverage of security risks than either framework alone. Here are some key benefits:
- Enhanced Risk Management: Combining NIST CSF’s cybersecurity focus with ISO 27001’s broader information security approach creates a more robust security posture.
- Improved Security Strategy: The different perspectives on similar security concerns in both frameworks can help identify blind spots and improve your overall security strategy.
- Balanced Security Program: Using both frameworks helps your organization address both technical security controls and governance processes.
- Demonstrated Security Diligence: A combined approach can help demonstrate security diligence to various stakeholders, including technical teams, executives, customers, and regulators.
Creating a Stronger Security Posture
Building your security program around both NIST CSF and ISO 27001 simultaneously will give you a stronger cybersecurity posture. This integrated approach not only enhances your security but also saves your business time and money in the long run.
It’s essential to note that while there are many similarities between the two frameworks, there are also differences. Neither NIST CSF nor ISO 27001 contains all the standards of the other, so it’s crucial not to assume that compliance with one automatically means compliance with the other.
By understanding and leveraging the complementary strengths of NIST CSF and ISO 27001, you can create a more comprehensive and effective cybersecurity strategy that protects your organization’s assets and data.
Implementation Process Comparison
When it comes to enhancing your organization’s security posture, understanding the implementation processes of NIST CSF and ISO 27001 is crucial. Both frameworks offer structured approaches to managing cybersecurity risks, but they differ in their implementation methodologies.
Steps to Implement NIST CSF
Implementing NIST CSF involves several key steps. First, you need to identify your organization’s current cybersecurity posture and understand the framework’s core functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. Next, you should conduct a risk assessment to determine your organization’s risk profile and prioritize cybersecurity efforts accordingly.
- Develop a roadmap for implementing the NIST CSF, focusing on high-priority areas.
- Implement the necessary cybersecurity controls and measures.
- Continuously monitor and assess your cybersecurity posture, making adjustments as needed.
Steps to Achieve ISO 27001 Certification
Achieving ISO 27001 certification involves a more formalized process. The journey begins with a Gap Assessment, where you review your organization’s current Information Security Management System (ISMS) against ISO 27001 requirements. This is followed by the implementation phase, where you develop and implement the necessary policies, procedures, and controls to address identified gaps.
- Gap Assessment: Identify gaps in your current ISMS relative to ISO 27001 requirements.
- Implementation: Develop and implement necessary policies, procedures, and controls.
- Internal Audit: Conduct an internal audit to ensure your ISMS conforms to ISO 27001.
- Stage 1 Audit (Document Review): An external auditor reviews your documentation.
- Stage 2 Audit (Certification Audit): The external auditor assesses the implementation of your ISMS.
Upon successful completion of the Stage 2 Audit, your organization is awarded ISO 27001 certification. To maintain certification, you’ll need to undergo annual surveillance audits and a recertification audit every three years.
Conclusion
In the realm of cybersecurity, both NIST CSF and ISO 27001 stand out as significant frameworks that can bolster your organization’s security posture. As you’ve seen, both offer valuable roadmaps for enhancing cybersecurity and information security management systems.
NIST CSF empowers organizations to manage cybersecurity risks effectively with a flexible and scalable approach. On the other hand, ISO 27001 guides companies in building a comprehensive Information Security Management System (ISMS) that aligns with core business objectives. By considering compliance with either framework, your organization can benefit from improved security and resilience, aligning strategically with your business goals.
Now that you’ve gained a comprehensive understanding of both NIST CSF and ISO 27001, their similarities, differences, and how they can complement each other, you’re better equipped to make an informed decision. The key considerations include your organizational maturity, business requirements, and available resources. Both frameworks share the fundamental goal of improving your organization’s security posture and protecting critical information assets.
It’s essential to recognize that the choice between NIST CSF and ISO 27001 isn’t necessarily an either/or decision; many organizations implement both frameworks in complementary ways. View compliance as a journey rather than a destination, with continuous improvement being the ultimate goal, regardless of which framework you choose.
As you begin your implementation journey, whether you choose NIST CSF, ISO 27001, or a combined approach, you’ll be taking a significant step the way towards enhancing your cybersecurity. Both NIST CSF and ISO 27001 can guide you the way to a more robust security posture. By adopting either or both of these frameworks, you’re investing in your organization’s future way of managing cybersecurity risks.